Section Links
“Remember: Don't forget to order a new planner each year”
Managing – Lameness
Lameness is an extremely common problem in most flocks' management is important to minimise the discomfort to the sheep (welfare) and also to avoid loss in production. Lameness is a major welfare concern in sheep farming and has economic impact on the flock performance.
For information about the management and control of Foot Rot - Click here for a PDF
A highly useful resource is also available via the following link- www.footrotinsheep.org
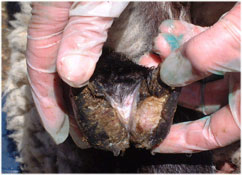 Common causes:
Common causes:
- Foot rot and Scald
- Interdigital problems e.g. soil and grass ‘balling'
- Separation of the hoof wall
- Infections and abscesses.
- Overgrowth of hoof leading to splitting and infection.
Other causes:
- Injury
- Joint ill
- Post dipping lameness
General advice
- Make sure you know what is causing lameness - get a diagnosis from your Vet the right treatments are used
- Assess the incidence of lameness and set out a control plan with targets
- Segregate lame sheep for treatment and to minimise spread of infection
- Treat foot rot quickly, don't leave lame sheep to infect others
- Be prepared to cull persistently lame sheep
- Trim feet only if necessary. Do not routinely trim
- Consider vaccination as a part of the control programme

